To improve air conditioner efficiency, clean or replace filters regularly, ensure proper insulation, and schedule routine maintenance. Use a programmable thermostat and consider upgrading to an energy-efficient model for cost-effective cooling.
Exploring the realm of cooling comfort, understanding air conditioner efficiency is the key to a chilled haven. For beginners in the cooling game, deciphering the complexities of SEER ratings, energy consumption, and optimal performance might seem like navigating uncharted territory. Fear not! In this blog post, we unravel the mysteries of air conditioner efficiency, providing a beginner-friendly guide to help you make informed choices and keep your space cool without breaking the bank.
Importance of Air Conditioner Efficiency

The efficiency of an air conditioner is crucial for several reasons, and its importance extends to various aspects of individual comfort, environmental impact, and economic considerations. Here are some key reasons why air conditioner efficiency is important:
1. Energy Consumption and Cost Savings:
Efficient air conditioners consume less energy to cool a given space, resulting in lower electricity bills for homeowners and businesses.
Over the long term, investing in a high-efficiency air conditioner can lead to substantial cost savings on energy bills.
2. Environmental Impact:
Lower energy consumption means reduced greenhouse gas emissions and a smaller carbon footprint. Energy-efficient air conditioners contribute to environmental sustainability by helping combat climate change.
Compliance with energy efficiency standards and regulations also supports environmental conservation efforts.
3. Resource Conservation:
Energy-efficient air conditioners utilize resources more effectively, contributing to the conservation of energy and reducing the strain on power generation and distribution infrastructure.
4. Comfort and Performance:
Efficient air conditioners cool spaces more effectively and maintain a consistent temperature, providing better comfort for occupants.
Improved performance can lead to faster cooling and better humidity control, enhancing overall indoor comfort.
5. Long-Term Durability and Reliability:
Well-designed and efficient air conditioning systems often have better build quality, leading to increased durability and reliability.
Reduced energy consumption can also result in less wear and tear on components, potentially extending the lifespan of the air conditioner.
6. Government and Utility Incentives:
Many governments and utility companies offer incentives, rebates, or tax credits for the installation of energy-efficient appliances, including air conditioners. This further encourages the adoption of efficient technologies.
7. Market Demand and Property Value:
Energy-efficient homes and buildings are becoming increasingly popular among consumers. Installing efficient air conditioning systems can enhance the market value and attractiveness of a property.
8. Reduced Peak Demand:
Efficient air conditioners contribute to lowering peak electricity demand, which can help prevent power outages and reduce the need for additional power generation infrastructure.
9. Adaptation to Climate Change:
As global temperatures rise, the demand for air conditioning is likely to increase. Energy-efficient systems help manage this increased demand without putting excessive strain on energy resources.
10. Technological Innovation:
The pursuit of higher efficiency standards drives innovation in air conditioning technology. This innovation can lead to the development of more advanced and sustainable cooling solutions.
In summary, air conditioner efficiency is crucial for economic, environmental, and comfort-related reasons. As the world focuses on sustainability and energy conservation, the importance of efficient air conditioning systems continues to grow.
Understanding Air Conditioner Efficiency
Air conditioner efficiency is a measure of how well an air conditioning system can convert energy into cooling. The efficiency of an air conditioner is crucial for several reasons, including energy savings, environmental impact, and overall comfort. Here are some key concepts to help you understand air conditioner efficiency:
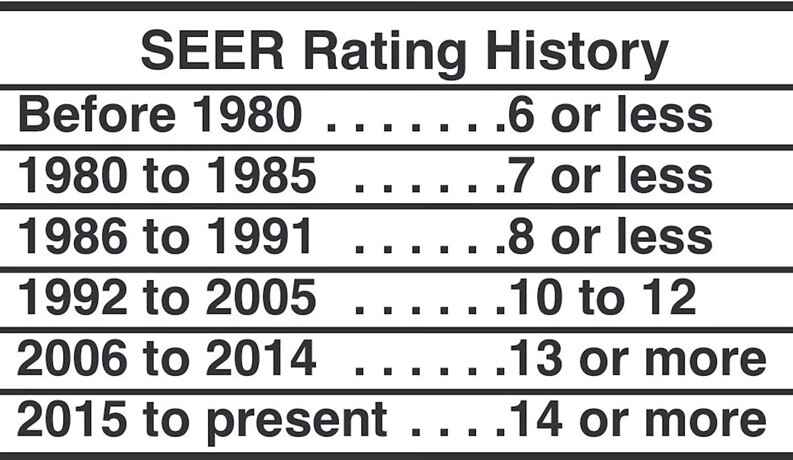
1. SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio):
SEER is a standard measurement used to rate the efficiency of air conditioners. It represents the total cooling output (measured in BTUs) during a typical cooling season, divided by the total electric energy input (measured in watt-hours) during the same period.
Higher SEER ratings indicate higher efficiency. Newer models often have higher SEER ratings than older ones.
2. EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio):
EER is similar to SEER but is a ratio of cooling output to energy input at a specific outdoor temperature (usually 95°F or 35°C). It does not vary with the season.
EER is a useful metric for understanding how well an air conditioner performs under extreme conditions.
3. Inverter Technology:
Traditional air conditioners have fixed-speed compressors that turn on and off to maintain the desired temperature. In contrast, inverter technology allows the compressor to adjust its speed continuously, providing more precise temperature control and higher energy efficiency.
4. Energy Star Certification:
Energy Star is a program run by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) that certifies products meeting specific energy efficiency criteria. Air conditioners with the Energy Star label typically use 15% less energy than standard models.
5. Variable-Speed Motors:
Air handlers and fans with variable-speed motors can operate at different speeds depending on the cooling needs. This results in better efficiency and more consistent temperature control.
6. Proper Sizing and Installation:
An efficiently sized and well-installed air conditioning system ensures optimal performance. Undersized units may struggle to cool a space, while oversized units can lead to short cycling, reducing efficiency and comfort.
7. Maintenance:
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning or replacing filters, checking refrigerant levels, and cleaning coils, is essential for maintaining optimal efficiency.
8. Climate Considerations:
The climate in which the air conditioner operates affects its efficiency. Some units are designed to perform better in specific climates or conditions.
Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions when purchasing, using, and maintaining an air conditioning system. High-efficiency units may have a higher upfront cost but can result in significant long-term energy savings. Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications and consider seeking professional advice for the most accurate assessment of a system’s efficiency in your specific environment.
Factors Affecting Air Conditioner Efficiency
Several factors can affect the efficiency of an air conditioner. Understanding these factors is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and energy efficiency. Here are some key factors:
1. Size of the Air Conditioner:
An air conditioner that is too small for the space it is intended to cool will struggle to reach the desired temperature, leading to increased energy consumption and decreased efficiency. On the other hand, an oversized unit may short cycle, turning on and off frequently, which also reduces efficiency.
2. Insulation and Sealing:
The level of insulation in a building and the effectiveness of doors and windows in preventing air leakage can significantly impact the efficiency of an air conditioner. Poor insulation and air leaks force the system to work harder to maintain the desired temperature.
3. Thermostat Settings:
Setting the thermostat too low in the summer or too high in the winter can increase energy consumption. A programmable thermostat that adjusts temperatures based on occupancy and time of day can help optimize efficiency.
4. Air Filter Condition:
A dirty or clogged air filter restricts airflow, forcing the air conditioner to work harder to circulate air. Regularly changing or cleaning the air filter is essential for maintaining efficiency and indoor air quality.
5. Regular Maintenance:
Neglecting regular maintenance, such as cleaning coils, checking refrigerant levels, and ensuring all components are in good condition, can lead to reduced efficiency and higher energy consumption.
6. Age and Condition of the System:
Older air conditioning systems may not be as energy-efficient as newer models. Additionally, wear and tear over time can decrease the efficiency of the system. Upgrading to a newer, more energy-efficient model may be cost-effective in the long run.
7. Ventilation:
Proper ventilation is essential for allowing the conditioned air to circulate effectively. Blocked or closed vents can disrupt airflow, making the system work harder to cool or heat the space.
8. Location of the Outdoor Unit:
The outdoor unit (condenser) should be placed in a well-ventilated area with adequate clearance. If the unit is surrounded by obstructions or debris, it can hinder heat exchange and reduce efficiency.
9. Climate and Temperature:
The local climate and ambient temperature affect how hard the air conditioner needs to work. Extremely high or low temperatures can strain the system and reduce efficiency.
10. Usage Patterns:
The frequency and duration of air conditioner use impact energy consumption. Unnecessarily running the system or keeping it on when the space is unoccupied can waste energy.
Regular professional maintenance and attentive use can help address many of these factors and ensure that your air conditioner operates at its highest efficiency.
Smart Thermostats and Temperature Control

Introduction to Smart Thermostats
Smart thermostats are advanced heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) devices that use modern technology to enhance temperature control in homes and businesses. Unlike traditional thermostats, smart thermostats offer features such as remote access, learning capabilities, and integration with other smart home systems.
1. Remote Access:
Smart thermostats can be controlled remotely using smartphones, tablets, or other internet-connected devices. This allows users to adjust the temperature settings even when they are away from home, providing convenience and energy savings.
2. Learning Capabilities:
Many smart thermostats are equipped with learning algorithms that analyze user behavior and adapt to the occupants’ preferences over time. This feature helps optimize energy usage by automatically adjusting temperature settings based on daily routines and habits.
3. Integration with Smart Home Systems:
Smart thermostats can often be integrated into broader smart home ecosystems. They may work with voice-activated assistants like Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant, allowing users to control the thermostat using voice commands. Integration with other smart devices, such as smart lighting or security systems, can create a more cohesive and efficient smart home environment.
Benefits of Using Smart Thermostats
1. Energy Efficiency:
One of the primary benefits of smart thermostats is their ability to enhance energy efficiency. The learning capabilities and remote access features enable users to optimize heating and cooling schedules, resulting in reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills.
2. Cost Savings:
By efficiently managing heating and cooling, smart thermostats help users save on energy costs. The ability to monitor and control HVAC systems remotely allows users to make real-time adjustments, avoiding unnecessary energy expenditure when the system is not needed.
3. Environmental Impact:
Reduced energy consumption not only saves money but also contributes to a smaller carbon footprint. Smart thermostats promote environmentally friendly practices by optimizing HVAC operations and minimizing energy waste.
4. Convenience:
The convenience of remote access and voice control simplifies temperature management. Users can make adjustments on the go, ensuring comfort upon returning home or when unexpected temperature changes occur.
5. Enhanced Comfort:
Smart thermostats contribute to improved comfort by adapting to users’ preferences. The learning algorithms ensure that the indoor environment aligns with occupants’ habits, providing a comfortable atmosphere without manual intervention.
6. Rebates and Incentives:
Many utility companies and governments offer rebates or incentives for installing energy-efficient devices, including smart thermostats. Taking advantage of these programs can further reduce the upfront cost of the device.
In conclusion, smart thermostats offer a range of benefits, including energy efficiency, cost savings, environmental impact reduction, convenience, enhanced comfort, and potential financial incentives. These devices are a key component of modern home automation, providing users with greater control over their HVAC systems while promoting sustainability and resource conservation.
Energy-Efficient Cooling Practices

Energy-efficient cooling practices are essential for optimizing air conditioner efficiency, reducing energy consumption, and lowering electricity bills. Here are some strategies related to ceiling fans, curtains/blinds, and shade/landscaping:
Proper Use of Ceiling Fans:
Direction of Rotation: Ensure that ceiling fans are set to rotate counterclockwise during the summer. This creates a breeze that helps cool the room occupants.
Temperature Adjustment: Use ceiling fans in conjunction with the air conditioner to distribute cooled air more effectively. This allows you to set the thermostat a few degrees higher while maintaining comfort.
Closing Curtains and Blinds during the Hottest Parts of the Day:
Solar Heat Gain: Close curtains and blinds on windows facing direct sunlight to reduce solar heat gain. This prevents the sun from heating up the interior of your home.
Reflective Materials: Choose curtains or blinds made from reflective materials to bounce sunlight away from the windows.
Strategic Use of Shade and Landscaping:
Planting Trees: Strategically plant trees on the west and east sides of your home to provide shade. Deciduous trees are ideal as they provide shade in the summer and allow sunlight in during the winter.
Awning Installation: Install awnings over windows, particularly on the west-facing side, to block direct sunlight and reduce heat absorption.
Use of Exterior Shading Devices: Consider exterior shading devices such as pergolas or shades to block sunlight and heat before it reaches your windows.
By incorporating these practices, you can minimize the reliance on your air conditioner and create a more energy-efficient and comfortable indoor environment. Additionally, adopting these strategies contributes to reducing your overall carbon footprint and promotes sustainable living.
Optimal Temperature Settings

Recommended Temperature Settings for Comfort and Efficiency:
Maintaining the right temperature settings for your air conditioner not only ensures comfort but also contributes to energy efficiency. Here are some recommended temperature settings for different scenarios:
1. Normal Occupancy:
During hot summer months, set the thermostat to around 78°F (25-26°C) when you are at home and active.
In milder weather, consider setting the thermostat a bit higher for additional energy savings.
2. Sleeping Hours:
To promote a comfortable sleep environment, aim for a slightly warmer temperature, around 72-76°F (22-24°C).
3. Away from Home:
When leaving the house for an extended period, increase the thermostat setting to reduce energy consumption. A setting of 85°F (29°C) is recommended to balance energy savings with preventing excessive heat buildup.
4. Humidity Control:
Use the AC’s “auto” mode or a dehumidifier to maintain indoor humidity levels between 30-50%. This helps improve comfort and can allow you to set the thermostat a bit higher without sacrificing comfort.
5. Smart Thermostats:
Consider investing in a smart thermostat that can automatically adjust temperature settings based on your preferences and daily routine. This can optimize comfort and energy efficiency without manual intervention.
Adjusting Thermostat Settings When Away from Home:
1. Programmable Thermostats:
If you have a programmable thermostat, take advantage of its features to create a schedule that adjusts the temperature when you are away from home.
Raise the temperature when you leave for work and lower it before you return.
2. Manual Adjustment:
If you don’t have a programmable thermostat, make it a habit to manually adjust the temperature before leaving the house. Raise the temperature in summer and lower it in winter to reduce unnecessary energy consumption.
3. Vacation Mode:
When going on vacation, set the thermostat to a temperature that minimizes energy usage while preventing extreme temperatures in the house. Aim for around 85°F (29°C) in the summer and 55°F (13°C) in the winter.
4. Remote Access:
Some modern thermostats offer remote access through smartphone apps. Take advantage of this feature to adjust the temperature settings while you’re away, ensuring energy efficiency without compromising comfort upon your return.
By following these guidelines and adjusting your air conditioner settings based on occupancy and external factors, you can achieve a balance between comfort and energy efficiency, ultimately reducing your energy bills and environmental impact.
Utilizing Programmable Features

Utilizing programmable features for air conditioner efficiency is a smart approach to optimize energy usage and maintain a comfortable environment. Here are some strategies for programming thermostat settings and creating cooling schedules:
Programming Thermostat for Different Times of the Day:
Modern air conditioners often come equipped with programmable thermostats that allow users to set different temperatures for various times of the day.
Benefits:
Energy Efficiency: By adjusting the temperature based on your daily routine, you can optimize energy usage and reduce overall electricity costs.
Comfort: Ensure a comfortable indoor environment when you’re at home while saving energy when the space is unoccupied.
Steps to Program Thermostat:
Identify Daily Patterns: Analyze your daily routine to determine when you are typically at home, away, or asleep.
Set Temperatures Accordingly: Program the thermostat to increase the temperature when you’re away or asleep and lower it when you’re at home and active.
Smart Thermostats: Consider using smart thermostats that can learn your habits and adjust settings automatically.
Example Programming:
Morning (6 AM – 9 AM): 72°F for waking up and getting ready.
Daytime (9 AM – 5 PM): 80°F when you’re likely away at work.
Evening (5 PM – 10 PM): 75°F for when you’re back home and active.
Night (10 PM – 6 AM): 70°F for sleeping hours.
Creating Cooling Schedules:
Understanding Cooling Schedules:
Cooling schedules involve pre-setting the air conditioner to turn on and off at specific times to maintain desired temperatures.
Benefits:
Predictable Comfort: Ensure that your space is cool and comfortable when you need it without wasting energy when it’s unnecessary.
Cost Savings: By avoiding continuous operation, you can save on energy bills.
Steps to Create Cooling Schedules:
Identify Peak Usage Times: Determine when you typically need cooling the most and when it can be reduced.
Utilize Timer Features: Set the air conditioner’s timer or scheduling feature to turn on and off at specific times.
Consider Zoning: If your system supports it, create different cooling zones for various areas in your home.
Example Cooling Schedule:
Morning (6 AM – 9 AM): AC turns on to cool the house as you wake up.
Daytime (9 AM – 5 PM): AC turns off or operates at a higher temperature when you’re away.
Evening (5 PM – 10 PM): AC resumes cooling for your return home.
Night (10 PM – 6 AM): AC operates at a moderate level for a comfortable sleeping environment.
By incorporating these programmable features, you can enhance the efficiency of your air conditioner, making it both cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
Investing in Energy-Efficient Equipment

Overview of Energy Star Rated Air Conditioners
Energy Star is a program established by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to promote energy efficiency and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. When it comes to air conditioners, Energy Star-rated units are designed to meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the EPA. Investing in Energy Star-rated air conditioners can offer various benefits:
Energy Efficiency:
Energy Star-rated air conditioners are designed to be more energy-efficient than standard models. They often use advanced technologies and components to maximize cooling performance while minimizing energy consumption.
Cost Savings:
Due to their energy efficiency, Energy Star-rated air conditioners can help lower energy bills. While the initial cost may be higher, the long-term savings in energy expenses can outweigh the upfront investment.
Environmental Impact:
Using energy-efficient appliances helps reduce carbon emissions and lowers the overall environmental impact. Energy Star-rated air conditioners contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly approach to cooling.
Incentives and Rebates:
Many governments and utility companies offer incentives or rebates for the purchase of Energy Star-rated appliances. This can further reduce the overall cost of upgrading to a more energy-efficient air conditioner.
Performance Standards:
Energy Star sets performance standards that go beyond just energy efficiency. These standards also consider factors such as comfort, noise levels, and overall product quality.
Considerations When Upgrading to a New Unit

When considering upgrading to a new air conditioning unit, several factors should be taken into account to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency:
Correct Sizing:
It’s crucial to choose an air conditioner that is appropriately sized for the space it will cool. An undersized unit will struggle to cool the area, while an oversized unit may cycle on and off frequently, leading to inefficiency and increased wear and tear.
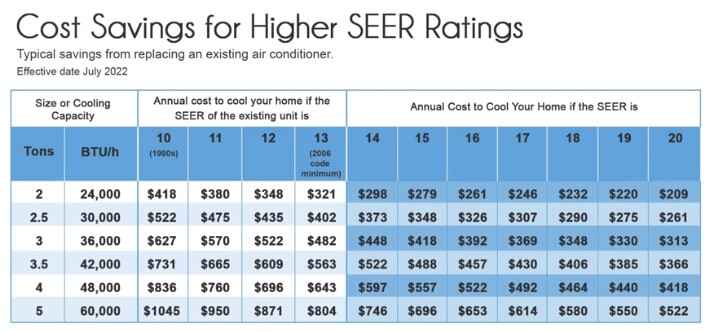
Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) and Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER):
These ratings indicate the energy efficiency of the air conditioner. A higher EER or SEER rating signifies better energy performance. Energy Star-rated units typically meet or exceed these efficiency standards.
Technology and Features:
Look for advanced technologies such as variable-speed compressors, programmable thermostats, and smart controls. These features can enhance energy efficiency and overall performance.
Maintenance Requirements:
Regular maintenance is essential for the optimal functioning of any air conditioning unit. Choose a model with easy access to filters and coils for straightforward cleaning and maintenance.
Installation Quality:
Proper installation is critical for the efficient operation of an air conditioner. Ensure that the new unit is installed by a qualified professional to maximize its performance and longevity.
Investing in energy-efficient air conditioning equipment not only benefits your immediate comfort but also contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future. Consider Energy Star-rated models and weigh the various factors involved to make an informed decision when upgrading your air conditioning system.
Incorporating Smart Home Integration
Incorporating smart home integration for air conditioner efficiency involves connecting your air conditioning system with various technologies to enhance control, energy efficiency, and user experience. Two key aspects of this integration are:
Integration with Home Automation Systems:
Smart Thermostats:
Replace or upgrade your existing thermostat with a smart thermostat. These devices allow for remote control through mobile apps, enabling users to adjust temperature settings from anywhere.
Sensors and Automation:
Integrate temperature and occupancy sensors to optimize cooling based on real-time conditions. For instance, the system can automatically adjust settings when no one is at home or when certain rooms are unoccupied.
Integration Platforms:
Utilize popular home automation platforms like Apple HomeKit, Google Home, or Amazon Alexa. This allows users to control the air conditioner through a centralized platform, enhancing ease of use.
Compatibility with Voice Assistants:
Voice Control:
Enable voice commands for controlling the air conditioner. Users can adjust temperature, set schedules, or turn the system on/off using voice commands.
Integration with Popular Voice Assistants:
Ensure compatibility with widely used voice assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, or Apple’s Siri. This broadens the accessibility and user base for your smart air conditioning system.
Natural Language Processing:
Implement natural language processing capabilities to enhance the user experience. This allows users to communicate with the air conditioner in a more conversational manner.
Benefits of Smart Home Integration for Air Conditioner Efficiency:
Energy Savings:
Smart integration allows for more precise control, ensuring the air conditioner operates efficiently and only when necessary, leading to energy savings.
Convenience:
Users can control the air conditioner remotely, set schedules, and receive notifications, enhancing overall convenience and flexibility.
Optimized Comfort:
Sensors and automation can adapt to user preferences and environmental conditions, creating a comfortable living environment.
Interoperability:
Compatibility with popular platforms and voice assistants ensures seamless integration into existing smart home ecosystems.
Data Insights:
Collect data on usage patterns and energy consumption, providing valuable insights for users to make informed decisions about energy usage and efficiency.
By focusing on these aspects, you can create a smart air conditioning system that not only enhances energy efficiency but also provides a user-friendly and interconnected experience within the broader smart home ecosystem.
Regular Maintenance Tips

Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the efficient functioning of your air conditioner. Here are some tips for maintaining your AC unit:
Cleaning and Changing Air Filters:
Frequency: Regularly clean or replace air filters every 1-3 months, or as recommended by the manufacturer.
Benefits: Improves airflow, enhances indoor air quality, and helps the system operate more efficiently.
Clearing and Cleaning Condenser Coils:
Clear Debris: Remove debris, leaves, and other obstructions from around the condenser unit.
Cleaning: Periodically clean condenser coils using a soft brush or low-pressure water to ensure optimal heat exchange.
Checking and Sealing Ductwork:
Inspection: Regularly inspect ductwork for leaks, loose connections, or any damage.
Sealing: Use duct sealant or metal tape to seal any leaks, preventing energy loss and maintaining system efficiency.
Lubricating Moving Parts:
Lubrication: Lubricate moving parts, such as fan motors and other bearings, as recommended by the manufacturer.
Benefits: Reduces friction, lowers energy consumption, and extends the lifespan of the components.
Schedule Professional HVAC Maintenance:
Annual Checkup: Arrange for a professional HVAC technician to perform annual maintenance.
Comprehensive Inspection: A technician can inspect and tune up the entire system, ensuring optimal performance and catching potential issues early.
Remember to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and consult with a professional if you are unsure about any maintenance task. Consistent maintenance not only improves the efficiency of your air conditioner but also extends its lifespan and helps prevent costly repairs.
Tips for Improving Air Conditioner Efficiency

Improving the efficiency of your air conditioner not only helps reduce energy consumption but also contributes to lower utility bills and a smaller environmental footprint. Here are some tips to enhance the efficiency of your air conditioning system:
Regular Maintenance Practices:
Clean or Replace Filters: Dirty filters restrict airflow, reducing the efficiency of your air conditioner. Clean or replace filters regularly, ideally every 1-3 months.
Coil Cleaning: The evaporator and condenser coils can accumulate dirt over time, affecting heat exchange. Regularly clean these coils to maintain optimal efficiency.
Check and Seal Ducts: Leaky ducts can lead to significant energy losses. Inspect and seal any leaks in the ductwork to ensure efficient air circulation.
Inspect Refrigerant Levels: Low refrigerant levels can decrease the efficiency of your AC unit. Schedule professional maintenance to check and recharge refrigerant levels as needed.
Clear Condensate Drains: Clogged condensate drains can lead to increased humidity levels and potential water damage. Ensure drains are clear to maintain proper moisture removal.
Optimal Thermostat Settings:
Programmable Thermostat: Use a programmable thermostat to set different temperatures for various times of the day. This helps reduce energy consumption when cooling is not essential, such as when you’re away or sleeping.
Recommended Temperature Settings: Keep your thermostat set to the recommended temperatures for energy efficiency. In warmer months, aim for around 78°F (25-26°C) when you’re at home and slightly higher when you’re away.
Avoid Drastic Temperature Changes: Set your thermostat to a moderate temperature to avoid overworking the system. Drastic temperature changes can lead to increased energy consumption.
Consideration of Climate and Weather Conditions:
Utilize Natural Ventilation: Take advantage of cooler evenings or mornings by turning off the air conditioner and opening windows. Use fans to circulate fresh air throughout your home.
Use Curtains or Blinds: Block out sunlight during the hottest parts of the day to reduce the heat entering your home. This can lessen the workload on your air conditioner.
Shade Your Outdoor Unit: If possible, provide shade for the outdoor condenser unit. This helps the unit operate more efficiently by preventing it from working in direct sunlight.
Adjust Thermostat When Away: When leaving for an extended period, consider adjusting your thermostat to a higher temperature. There’s no need to cool an empty house, and this can result in energy savings.
By incorporating these maintenance practices and optimizing your thermostat settings based on climate conditions, you can enhance the efficiency of your air conditioner, leading to energy savings and a more comfortable indoor environment.
Financial and Environmental Implications

Cost Savings with High-Efficiency Units
Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Savings:
High-efficiency air conditioners may have a higher upfront cost, but their long-term operational expenses are typically lower.
Considerations of lifespan, maintenance costs, and energy savings should be factored in when evaluating the initial investment versus long-term savings.
Return on Investment in Energy-efficient Models:
Calculate the payback period for high-efficiency units by comparing energy savings against the additional initial cost.
Explore government incentives, tax credits, or rebates that can further enhance the return on investment and make energy-efficient models more financially appealing.
Environmental Benefits
Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
High-efficiency air conditioners consume less energy, resulting in reduced carbon dioxide emissions and other pollutants.
Quantify the environmental impact by comparing the emissions of high-efficiency units with standard models over their respective lifetimes.
Contribution to Sustainable Living:
Highlight the role of energy-efficient air conditioners in promoting sustainable living practices.
Emphasize the connection between reduced energy consumption and a lower overall environmental footprint, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
By addressing both financial and environmental aspects, consumers can make informed decisions that not only save them money in the long run but also contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly lifestyle.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and optimizing air conditioner efficiency is crucial for both environmental sustainability and cost-effective cooling. By implementing the discussed tips, such as regular maintenance, proper insulation, and smart technology utilization, you not only contribute to reducing your carbon footprint but also save on energy bills. Striking a balance between comfort and conservation is the key to a more efficient and eco-friendly cooling experience. Embracing these practices ensures that our reliance on air conditioning aligns with the broader goal of creating a greener and more sustainable future. Stay cool, stay efficient!







39 Comments