To fix a loose electrical connection, turn off power, identify the loose wire, tighten the screw or connector, and secure it with a screwdriver or pliers. Ensure a snug fit to prevent future issues.
Facing a loose electrical connection can be unnerving, but fret not – resolving it is simpler than you think. In this guide, we’ll demystify the process for beginners, providing a step-by-step walkthrough on how to fix a loose electrical connection. Whether it’s a plug, socket, or wiring, understanding the basics of tightening connections ensures a safe and efficient electrical system. Let’s dive into the essentials and empower you to tackle this common issue with confidence.
Risks and Hazards of Neglected Loose Electrical Connections
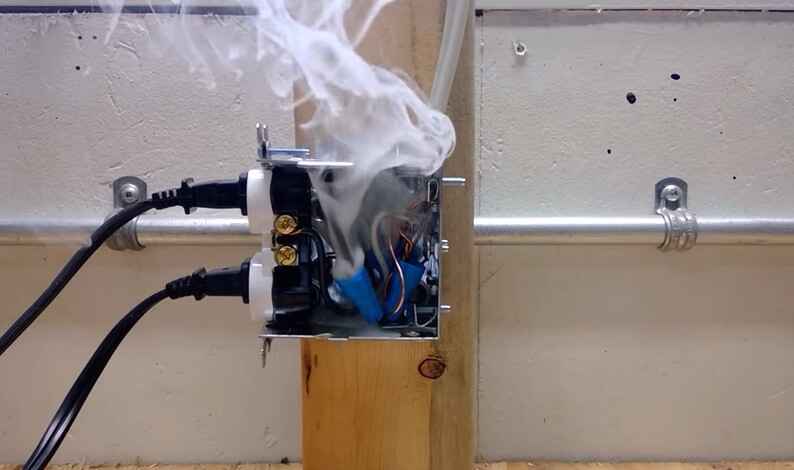

Neglected loose electrical connections pose serious risks and hazards in various settings, including residential, commercial, and industrial environments. Here are some potential risks and dangers associated with neglected loose electrical connections:
1. Fire Hazard:
Loose connections can create arcing and sparking, leading to the generation of heat.
Excessive heat can cause insulation materials to degrade, potentially leading to a fire.
Loose connections increase the risk of electrical arcs, which can ignite nearby flammable materials.
2. Electrocution:
Loose connections can result in an uneven flow of electricity, leading to electric shock hazards.
Touching or coming into contact with exposed live wires due to loose connections can cause serious injury or even death.
3. Equipment Damage:
Loose electrical connections can cause voltage fluctuations and power surges, damaging connected electrical devices and equipment.
In industrial settings, damaged equipment can lead to production downtime and financial losses.
4. Voltage Drop:
Loose connections can increase resistance in the circuit, leading to voltage drop.
Voltage drop can affect the performance of electrical devices and equipment, causing them to operate inefficiently or malfunction.
5. Unreliable Electrical Systems:
Loose connections can result in intermittent power failures and disruptions.
Unreliable electrical systems can lead to operational issues and safety concerns, particularly in critical environments such as hospitals or data centers.
6. Increased Energy Consumption:
Poorly connected electrical systems may require more energy to overcome increased resistance, leading to higher energy consumption and increased utility costs.
7. Corrosion and Oxidation:
Loose connections can allow moisture and contaminants to enter the connection points, leading to corrosion and oxidation.
Corroded connections further increase resistance and contribute to the degradation of the electrical system.
8. Code Violations and Legal Consequences:
Neglected loose electrical connections can lead to code violations, which may result in legal consequences and fines.
Compliance with electrical codes and standards is crucial for ensuring the safety of occupants and the proper functioning of electrical systems.
9. Hidden Hazards:
Loose connections may not always be visible, making it challenging to identify and address them.
Hidden hazards can pose a significant risk, especially if they are not detected and rectified promptly.
Regular inspection, maintenance, and adherence to electrical safety standards are essential to identifying and addressing loose electrical connections, mitigating the associated risks, and ensuring the overall safety and reliability of electrical systems. If you suspect or identify loose connections, it is crucial to consult with a qualified electrician to address the issues promptly.
Importance of secure electrical connections
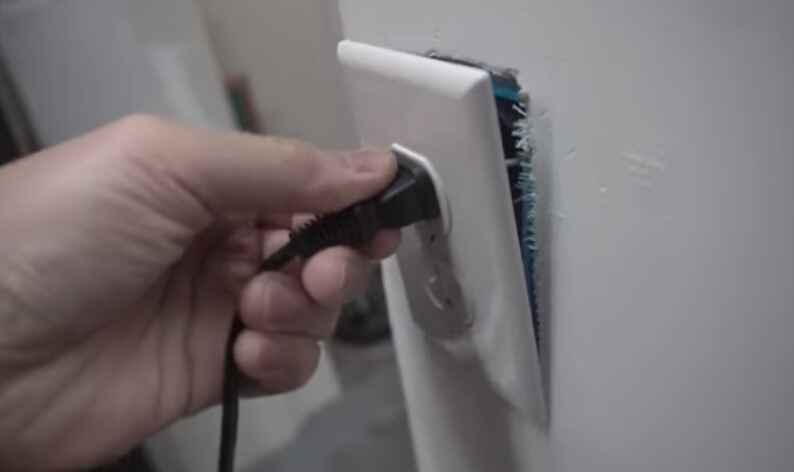

Secure electrical connections are crucial for various reasons, primarily related to safety, reliability, and efficient electrical performance. Here are some key reasons highlighting the importance of secure electrical connections:
1. Safety:
Prevention of Electrical Fires: Loose or insecure connections can result in overheating, which increases the risk of electrical fires. A secure connection ensures that current flows smoothly without generating excess heat.
Avoidance of Electrical Shocks: Loose connections can lead to exposed wires or contacts, increasing the risk of electric shock to individuals who come into contact with the electrical system.
2. Reliability:
Consistent Power Supply: Secure connections ensure a consistent flow of electricity. Unstable connections can cause intermittent power supply, leading to disruptions in electrical devices and systems.
Prevention of Downtime: In industrial settings, unreliable connections can lead to equipment failure and unplanned downtime, resulting in production losses and increased maintenance costs.
3. Efficiency:
Optimal Electrical Performance: Properly secured connections minimize resistance and impedance, allowing electrical systems to operate at their designed efficiency. Loose connections can increase resistance, leading to energy losses in the form of heat.
Reduced Energy Consumption: Efficient connections contribute to lower energy consumption because less energy is wasted as heat in the electrical system.
4. Longevity of Equipment:
Prevention of Equipment Damage: Secure connections prevent arcing and sparking, which can damage sensitive electronic components and devices over time.
Extended Equipment Lifespan: Properly maintained and secured electrical connections contribute to the longevity of electrical equipment and reduce the need for frequent replacements.
5. Compliance with Regulations:
Electrical Code Compliance: Many countries and regions have electrical codes and standards that mandate secure electrical connections. Adhering to these regulations is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical installations.
6. Cost Savings:
Reduced Maintenance Costs: Regularly inspecting and maintaining secure connections can prevent costly repairs and replacements associated with damaged equipment caused by poor connections.
Minimized Energy Costs: Secure connections contribute to energy efficiency, leading to lower energy bills over the long term.
7. Environmental Impact:
Energy Efficiency: By ensuring secure connections and minimizing energy losses, there is a positive impact on the environment, as reduced energy consumption contributes to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
In summary, secure electrical connections are fundamental for ensuring the safety, reliability, efficiency, and longevity of electrical systems and equipment. Regular inspections, proper installation practices, and adherence to electrical codes and standards are essential for maintaining secure connections.
Signs of a Loose Electrical Connection
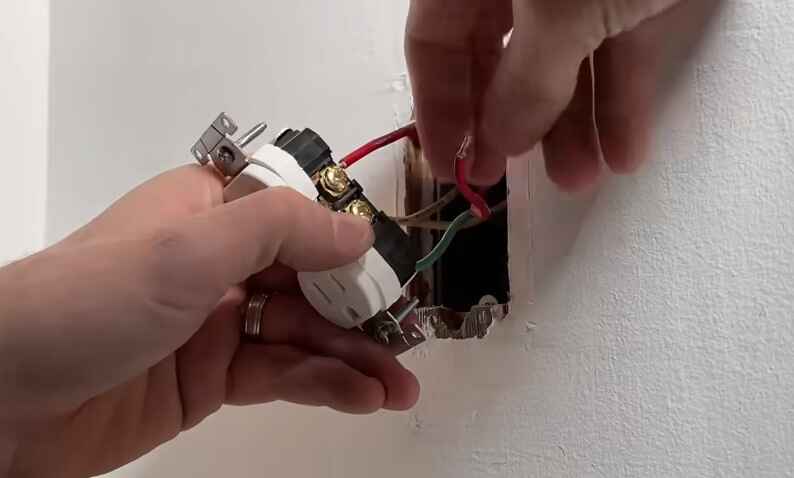

Loose electrical connections can pose serious safety hazards and should be addressed promptly. Here are some signs that may indicate a loose electrical connection:
1. Flickering Lights:
If lights flicker or dim without an obvious reason (like a bulb reaching the end of its life), it could be a sign of a loose connection in the electrical circuit.
2. Sparks or Arcing:
Visible sparks or arcing at an electrical outlet, switch, or any other connection point is a clear indication of a loose connection. This is a serious issue and requires immediate attention.
3. Hot Outlets or Switches:
If an outlet or switch feels unusually warm or hot to the touch, it may be a sign of a loose connection. Heat is generated when electrical resistance increases, which can happen with a poor connection.
4. Burn Marks or Discoloration:
Burn marks or discoloration around outlets, switches, or electrical panels suggest overheating, which can result from loose connections. This is a serious issue and should be addressed promptly to prevent a potential fire hazard.
5. Intermittent Power:
If power to a device or appliance is intermittent, it could be due to a loose connection in the wiring supplying power to that device.
6. Tripped Circuit Breakers or Blown Fuses:
Frequent tripping of circuit breakers or blown fuses may indicate an issue with the electrical system, including loose connections.
7. Crackling Sounds:
Unusual crackling or buzzing sounds coming from outlets or switches could be a sign of electrical arcing caused by loose connections.
8. Burning Smell:
A burning smell, especially near electrical outlets or appliances, can indicate overheating and a potential fire hazard due to loose connections.
9. Vibration or Movement:
If there is movement or vibration near electrical connections, such as wires or outlets, it can cause the connections to loosen over time.
10. Loose Outlets or Switches:
Physically loose outlets or switches may suggest that the internal wiring connections are also loose.
If you notice any of these signs, it’s crucial to address the issue promptly to prevent potential safety hazards. Electrical problems should be handled by qualified professionals, such as electricians, to ensure proper and safe repairs. Attempting to fix electrical issues without the necessary expertise can lead to further problems or, in extreme cases, electrical fires.
Safety precautions before attempting any electrical work

Working with electricity can be dangerous, so it’s crucial to take appropriate safety precautions to protect yourself and others. Here are some general safety guidelines to follow before attempting any electrical work:
1. Turn Off Power:
Always turn off the power at the circuit breaker or fuse box before starting any electrical work. Make sure the power is completely off by using a voltage tester.
2. Lock Out and Tag Out:
If possible, lock out and tag out the circuit you are working on to prevent someone from accidentally restoring power.
3. Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses, insulated gloves, and flame-resistant clothing, to protect yourself from potential hazards.
4. Inspect Tools and Equipment:
Ensure that your tools and equipment are in good condition. Check for any frayed cords, exposed wires, or damaged insulation. Use tools that are appropriate for the task at hand.
5. Stay Dry:
Avoid working on electrical components with wet hands or in damp conditions. Moisture increases the risk of electric shock.
6. Beware of Overhead Lines:
Be cautious of overhead power lines when working outside. Keep a safe distance to avoid accidental contact.
7. Understand the Electrical System:
Familiarize yourself with the electrical system in the area you are working on. Know the location of circuit breakers, fuse boxes, and emergency shut-off switches.
8. Use Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs):
Install GFCIs in areas where water and electricity may come into contact, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor outlets.
9. Follow Electrical Codes and Regulations:
Adhere to local electrical codes and regulations. They are designed to ensure safety standards are met.
10. Work with a Buddy:
If possible, have someone else present while you are working on electrical projects. In case of an emergency, they can provide assistance or call for help.
11. First Aid Kit:
Keep a well-stocked first aid kit nearby in case of minor injuries. Know the location of emergency exits and how to contact emergency services.
12. Educate Yourself:
Ensure you have a good understanding of the electrical work you are about to undertake. If you are unsure, seek guidance from a qualified electrician.
Remember that electrical work should often be left to trained professionals. If you’re unsure about a task or if it involves complex wiring, it’s safer to hire a licensed electrician to do the job. Safety should always be the top priority when working with electricity.
Tools and Materials
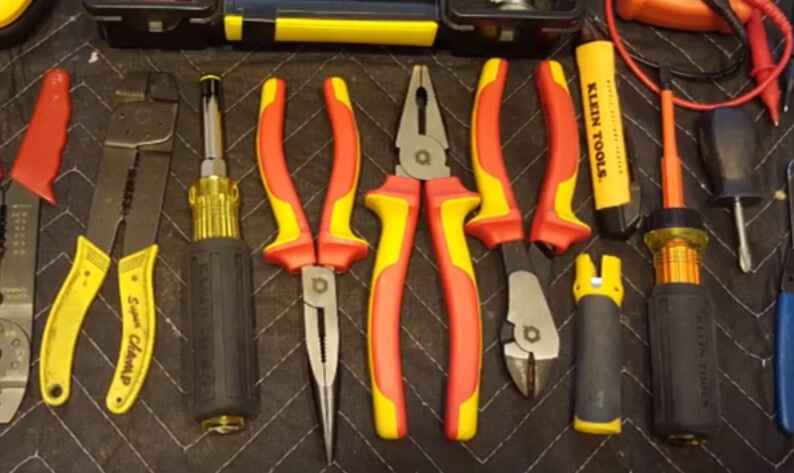

Fixing a loose electrical connection requires a combination of basic tools and insulation materials to ensure safety and proper repair. Here’s a list of tools and materials you might need:
A. Basic Tools:
1. Screwdrivers:
Flathead and Phillips screwdrivers for removing screws from electrical panels, outlets, switches, etc.
2. Pliers:
Needle-nose pliers for gripping and bending wires.
Wire-stripping pliers for safely removing insulation from wires.
3. Wire Cutter:
To cut and trim wires to the appropriate length.
4. Wire Connectors:
Twist-on wire connectors for securely joining wires.
B. Insulation Materials:
1. Electrical Tape:
Use high-quality electrical tape to insulate exposed wires and connections. Make sure it is rated for electrical applications.
2. Heat Shrink Tubing:
Provides a more secure and professional insulation method. Shrink tubing using a heat source like a heat gun.
3. Wire Nuts:
Another option for secure wire connections, especially in junction boxes.
C. Voltage Tester:
1. Non-Contact Voltage Tester:
A critical tool for checking if a circuit is live or if there is voltage present. Ensure your tester is functioning properly before use.
2. Multimeter:
A more versatile tool that can measure voltage, current, and resistance. Make sure it’s set to the appropriate function before use.
D. Additional Tools and Materials (Depending on the Situation):
1. Circuit Tester:
Helps identify whether a specific circuit is functioning correctly.
2. Crimping Tool:
For crimping connectors onto wires securely.
3. Flashlight:
Essential for better visibility, especially in dark or enclosed spaces.
4. Voltage Detector Pen:
Similar to a non-contact voltage tester, this pen-shaped tool detects the presence of voltage when touched to a wire or terminal.
5. Insulated Gloves:
Provides an extra layer of protection when working with electrical components.
Remember to prioritize safety when working with electricity. Turn off the power to the affected circuit before attempting any repairs, and double-check with your voltage tester to ensure the circuit is de-energized. If you are not comfortable or experienced with electrical work, it’s advisable to seek the help of a qualified electrician.
Identifying the Loose Electrical Connection
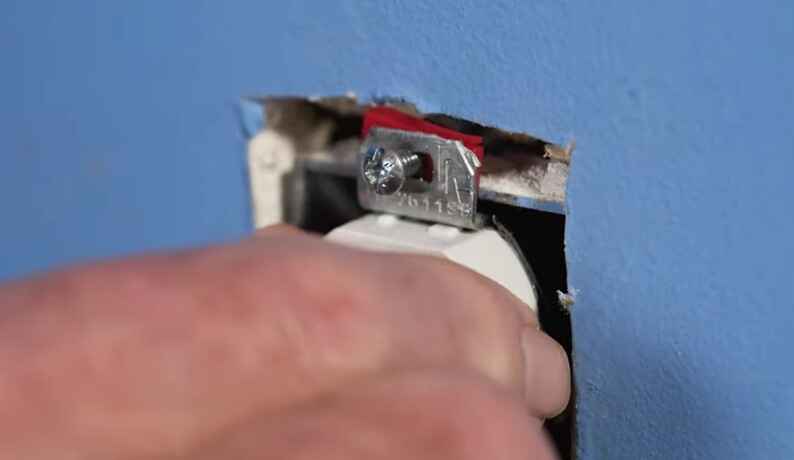

Identifying a loose electrical connection is crucial for maintaining a safe and functional electrical system. Here are some steps you can take to identify and address a loose electrical connection:
1. Visual Inspection:
Power Off: Before starting any inspection, make sure to turn off the power to the circuit you’re working on. This can involve switching off the circuit breaker or removing the fuse.
Inspect Outlets and Switches: Check outlets, switches, and other electrical devices for any signs of looseness. Look for gaps between the wall and the outlet or switch, which could indicate a loose connection.
2. Check Wiring:
Switches and Outlets: Remove the faceplate of switches and outlets and inspect the wiring. Loose wires may be visible or may fall out when touched.
Light Fixtures: If the issue is with a light fixture, check the wiring connections within the fixture.
3. Use a Circuit Tester:
A circuit tester or multimeter can help you identify loose connections. Ensure the power is off, then test the connections to see if they are secure. If the tester indicates an open circuit or inconsistent readings, it may be a sign of a loose connection.
4. Listen for Arcing or Buzzing Sounds:
Turn the power back on and listen for any unusual sounds like arcing or buzzing near electrical components. These sounds can indicate loose connections.
5. Check for Warmth:
Carefully touch electrical components (after ensuring the power is off) to see if any are warmer than they should be. Excessive heat can be a sign of a loose connection, which can cause resistance and heat buildup.
6. Inspect Circuit Breakers:
Loose connections within a circuit breaker panel can be dangerous. Inspect the connections within the panel for any signs of overheating or arcing.
7. Look for Burn Marks:
Burn marks on outlets, switches, or electrical panels can indicate a loose connection. If you see any, it’s crucial to address the issue promptly.
8. Tighten Connections:
If you identify a loose connection, tighten it using the appropriate tools. Be cautious and turn off the power before making any adjustments.
9. Seek Professional Help:
If you are unsure or uncomfortable dealing with electrical issues, it’s best to seek the help of a qualified electrician. Electrical work can be hazardous, and a professional can ensure the problem is addressed safely.
Remember, electrical work should be approached with caution, and if you are uncertain about any aspect of identifying or fixing a loose connection, it’s always best to consult with a licensed electrician.
Fixing a Loose Connection in Outlets
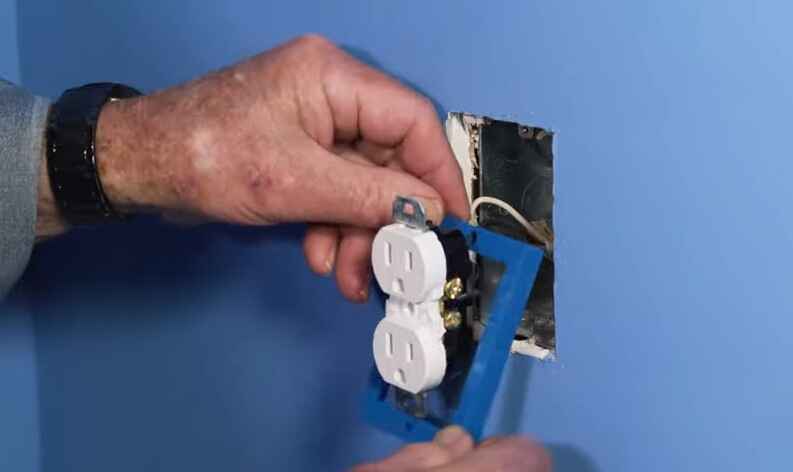

Fixing a loose electrical connection in outlets is important to ensure safety and proper functioning of the electrical system. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to address this issue:
Important Note: Ensure your safety by turning off the power before working on any electrical components. If you’re unsure or uncomfortable with electrical work, it’s best to hire a qualified electrician.
1. Turn off the Power:
Locate the circuit breaker or fuse box and turn off the power to the affected outlet. Double-check that the power is off by using a non-contact voltage tester.
2. Remove the Outlet Cover:
Unscrew and remove the outlet cover plate using a screwdriver.
3. Test the Wires:
Use a voltage tester to make sure the wires are not live. Test each wire to ensure there is no electrical current.
4. Remove the Outlet:
Carefully unscrew the outlet from the electrical box, taking note of the wiring configuration. Most outlets have screws on the top and bottom; loosen these screws to release the wires.
5. Inspect the Wires:
Check the wires for any signs of damage, such as fraying or burning. Trim any damaged sections if necessary.
6. Tighten the Screws:
If the wires are securely connected to the outlet but the connection is loose, tighten the screws that hold the wires in place. Make sure the wires are wrapped around the screws in a clockwise direction.
7. Replace the Outlet:
If the outlet itself is damaged or the connections are still loose, consider replacing the outlet with a new one. Make sure to match the wiring configuration of the old outlet.
8. Attach the Outlet:
Carefully attach the outlet back into the electrical box, securing it with the screws. Ensure the wires are properly connected and tightened.
9. Replace the Outlet Cover:
Screw the outlet cover plate back into place.
10. Turn on the Power:
Go back to the circuit breaker or fuse box and turn the power back on. Test the outlet with a voltage tester or plug in a small appliance to ensure it is functioning properly.
If, after following these steps, you still experience issues with the outlet, or if you’re uncomfortable with any part of this process, it’s recommended to contact a licensed electrician for assistance. Electrical work can be hazardous, and safety should always be the top priority.
Fixing a Loose Electrical Connection in Switches
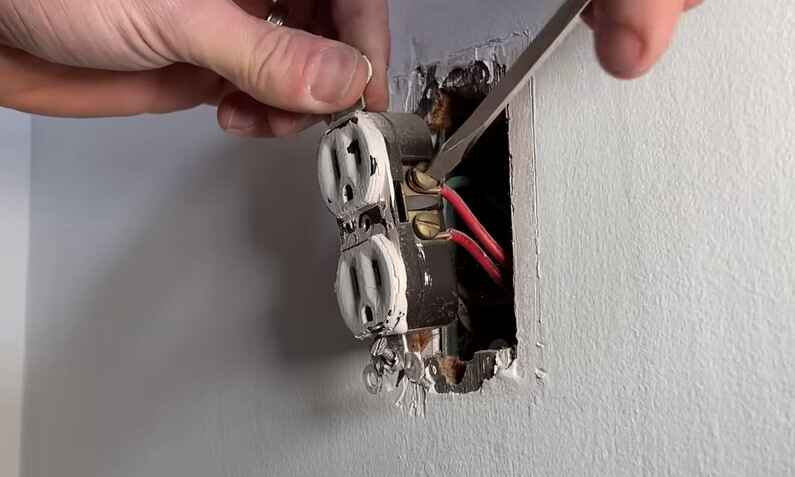

Fixing a loose electrical connection in switches is important to ensure proper electrical functionality and to prevent potential hazards. Here are some general steps you can follow to address this issue:
1. Turn Off Power:
Before working on any electrical connections, turn off the power to the circuit at the breaker box. This ensures your safety while working on the switch.
2. Use the Right Tools:
Gather the necessary tools, including a screwdriver, pliers, and a voltage tester. Make sure the tools are insulated to prevent electrical shock.
3. Remove the Switch Plate:
Unscrew and remove the switch plate cover using a screwdriver. This will expose the switch and its wiring.
4. Test for Power:
Use a voltage tester to check for the presence of electrical power. Confirm that the power is off by testing the wires connected to the switch.
5. Inspect the Connections:
Carefully inspect the connections on the switch. Look for any loose wires or screws. If you find any, tighten them using a screwdriver or pliers. Ensure that all connections are secure.
6. Replace the Switch:
If the switch itself is faulty, consider replacing it. To do this, disconnect the wires from the existing switch, unscrew it from the electrical box, and install a new switch. Make sure to connect the wires to the corresponding terminals on the new switch.
7. Check Wire Stripping:
Ensure that the wires are properly stripped and that there is enough bare wire exposed to make a secure connection. If needed, strip the wires to the appropriate length.
8. Use Terminal Screws:
If the switch has terminal screws, make sure the wires are securely fastened under the screws. If the switch uses push-in connectors, consider using the terminal screws instead for a more secure connection.
9. Secure the Ground Wire:
Confirm that the ground wire (usually a green or bare copper wire) is securely connected to the green grounding screw on the switch.
10. Reassemble and Test:
Once you have made the necessary adjustments, carefully reassemble the switch, and screw the switch plate cover back into place. Turn the power back on and test the switch to ensure it is working properly.
If you are unsure about any step or if you encounter any difficulties, it’s advisable to consult with a qualified electrician for assistance. Electrical work should be approached with caution to ensure safety and compliance with local electrical codes.
Fixing a Loose Electrical Connection in Light Fixtures
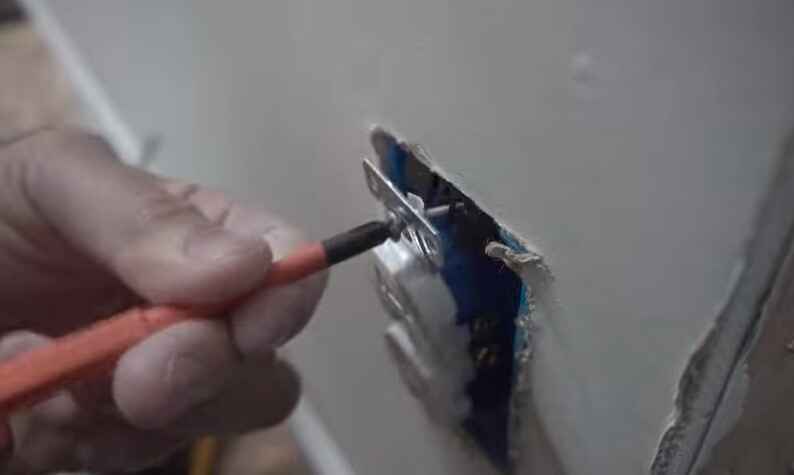

Fixing a loose electrical connection in a light fixture is important to prevent electrical hazards and ensure proper functionality. Here are the steps you can take to address this issue:
Important: Before working on any electrical components, make sure to turn off the power at the circuit breaker to ensure your safety. If you’re unsure, consult with a qualified electrician.
1. Turn Off Power:
Locate the circuit breaker that controls the power to the light fixture.
Turn off the power by flipping the corresponding circuit breaker to the “off” position.
2. Remove the Light Bulbs:
Take out any light bulbs from the fixture to avoid breakage or injury during the repair.
3. Remove the Fixture Cover:
If your light fixture has a cover, remove it by unscrewing the screws or gently pulling it off. Expose the wiring and the electrical connections.
4. Inspect the Wiring:
Carefully inspect the wiring and connections for any signs of damage or burn marks.
If you see any loose wires, tighten them using a screwdriver. If there are damaged wires, they may need to be replaced.
5. Check Wire Connections:
Ensure that all wire connections are secure.
If there are wire nuts, make sure they are tightly screwed on. If they are loose, remove the nut, trim the ends of the wires, and then reconnect them before reapplying the nut.
6. Tighten Screws:
Check for any loose screws on the fixture itself. Tighten them to ensure a secure connection.
7. Inspect the Electrical Box:
If the light fixture is mounted to an electrical box, ensure that the box is securely attached to the ceiling or wall.
Tighten any loose screws on the electrical box.
8. Replace Faulty Parts:
If you find any damaged components, such as frayed wires or a faulty socket, replace them with new parts. Ensure that the replacements are compatible with your fixture.
9. Reassemble the Fixture:
Once you’ve made the necessary repairs, reassemble the fixture. Screw the cover back on if applicable.
10. Restore Power:
Go back to the circuit breaker and turn the power back on.
11. Test the Fixture:
Install the light bulbs and turn on the fixture to ensure that it is working properly.
If you are uncomfortable or unsure about any step of this process, or if the problem persists, it’s advisable to seek the assistance of a qualified electrician to ensure the repair is done safely and effectively.
Testing the Connection
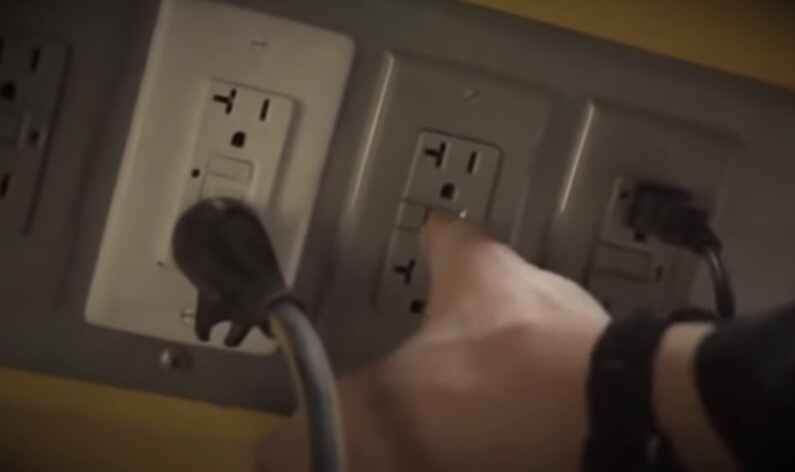

When testing a repaired loose electrical connection, you should follow a systematic approach to ensure safety and effectiveness. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Restoring power to the circuit:
Before restoring power, double-check your repair work to ensure that all connections are secure and no exposed wires are present.
If you had turned off power to the circuit during the repair, turn it back on. Ensure that the power source is stable and within the appropriate voltage range for the circuit.
2. Using a voltage tester to confirm a secure and safe connection:
Once power is restored, use a voltage tester to check the connection points for the presence of electrical voltage.
Ensure that the voltage tester is in good working condition.
Test the connection points carefully to confirm that the voltage is within the expected range and that there are no fluctuations or irregularities.
This step helps ensure that the electrical circuit is functioning properly and that there are no safety hazards.
3. Checking for any remaining issues:
After confirming a secure and safe connection with the voltage tester, visually inspect the repaired area for any signs of damage, overheating, or other abnormalities.
Look for any unusual sounds, smells, or other indicators that might suggest a problem.
If applicable, test the circuit by using the devices or equipment it powers to ensure proper functionality.
Monitor the repaired connection for some time to make sure there are no intermittent issues or unexpected behavior.
By following these steps, you can systematically test and verify the repaired electrical connection, ensuring both safety and functionality. Always prioritize safety, and if you are unsure or uncomfortable with any part of the process, it’s advisable to seek professional assistance.
Impact of Loose Electrical Connections on Air Conditioner Performance
Loose electrical connections in an air conditioning (AC) system can have several negative impacts on its efficiency, performance, lifespan, and various components. Here are some of the potential consequences:
1. AC Efficiency:
Loose electrical connections can result in increased electrical resistance. This increased resistance leads to higher energy consumption and reduced overall system efficiency.
Poor electrical connections can also cause voltage drops, making the AC system work harder to achieve the desired cooling, further decreasing efficiency.
2. AC Performance:
The compressor is a critical component of an AC system, and loose electrical connections can lead to inadequate power supply to the compressor motor. This can result in reduced compressor efficiency and compromised cooling performance.
3. AC Lifespan:
Continuous electrical issues, including loose connections, can contribute to premature wear and tear on electrical components. This may lead to a shorter lifespan for the AC system as a whole.
Components like capacitors, which are sensitive to electrical irregularities, may fail sooner if exposed to loose connections over an extended period.
4. AC Compressor:
The compressor is particularly vulnerable to electrical issues. Loose connections can cause the compressor to overheat, affecting its lubrication and potentially leading to compressor failure.
Unstable power supply due to loose connections can result in frequent starts and stops of the compressor, contributing to additional stress and wear.
5. AC Condenser:
Like the compressor, the condenser unit may experience reduced efficiency and cooling capacity due to poor electrical connections. This can result in insufficient heat exchange and, consequently, less effective cooling.
6. AC Fuse Box and Circuit Breaker:
Loose connections within the fuse box or circuit breaker can lead to electrical arcing, which can cause damage to the components and compromise the safety of the electrical system.
In extreme cases, loose connections can cause fuses to blow or circuit breakers to trip frequently, interrupting the operation of the AC system.
7. AC Short Cycling:
Loose connections may cause the AC system to short cycle, meaning it turns on and off more frequently than necessary. Short cycling not only reduces efficiency but also places additional stress on the components, potentially leading to premature failure.
When to Seek Professional Help

Recognizing when to seek professional help for fixing a loose electrical connection is crucial for ensuring safety and preventing further damage. Here are some factors to consider:
A. Recognizing when a DIY approach may not be sufficient:
1. Lack of Knowledge or Experience:
If you are not experienced or knowledgeable about electrical systems, it’s best to avoid attempting repairs. Working with electricity without the proper understanding can be dangerous.
2. Uncertain Cause:
If you’re unsure about the cause of the electrical issue or if it’s a recurring problem, it’s advisable to consult a professional. They can identify the root cause and address it effectively.
3. Multiple Affected Outlets or Fixtures:
If the problem extends beyond a single outlet or fixture, it may be a sign of a more complex issue within the electrical system. A professional can conduct a thorough assessment.
4. Tripped Circuit Breakers or Blown Fuses:
Frequent tripping of circuit breakers or blown fuses may indicate an underlying electrical problem that requires professional attention.
5. Visible Damage:
If you notice visible damage to wiring, outlets, or switches, such as burning, charring, or melting, it’s a clear indication that professional help is needed.
6. Strange Odors or Sounds:
Burning smells, buzzing sounds, or other unusual signs should not be ignored. These could be indicators of a serious electrical problem that requires immediate attention.
B. Importance of consulting a licensed electrician for complex issues:
1. Compliance with Codes and Standards:
Licensed electricians are trained to work in compliance with electrical codes and safety standards. This is essential to ensure the safety of your home and its occupants.
2. Complex Wiring Systems:
If your home has a complex wiring system or if the issue involves the main electrical panel, it’s best to hire a licensed electrician. They have the expertise to navigate intricate electrical setups.
3. Legal Requirements:
Some jurisdictions require electrical work to be performed by licensed professionals. Hiring a licensed electrician ensures that the work meets legal requirements and building codes.
4. Insurance Coverage:
In some cases, insurance may only cover damages or incidents if the electrical work was carried out by a licensed professional. DIY repairs might void insurance coverage in certain situations.
5. Long-Term Reliability:
Professional electricians have the knowledge and experience to provide long-term solutions. They can address not only the immediate issue but also identify and fix potential future problems.
Remember, electrical issues can pose serious safety risks. If you’re uncertain or uncomfortable dealing with a loose electrical connection, it’s always best to seek the expertise of a licensed electrician to ensure the safety and integrity of your electrical system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, addressing a loose electrical connection is crucial for both safety and functionality. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can effectively troubleshoot and remedy the issue. Remember to prioritize safety by disconnecting power, identifying the loose connection, and securing it properly. Regular maintenance and vigilance in detecting and addressing electrical problems can prevent potential hazards and ensure the smooth operation of your electrical systems. Don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance if needed, as safety should always be the top priority when dealing with electrical issues.






39 Comments